Introduction To Business Summary Template
When writing a business plan, it’s easy to get lost in the details to demonstrate how you’ve studied the ins and outs of the marketplace and have crunched every conceivable number. But, really, writing a hundred plus page business plan is not the best use of your energy.
It is a worthwhile exercise for an entrepreneur to bring out your business in such detail that no information is skipped. But the truth is that no one will ever spend their time reading it whether you’re competing in a business plan competition or trying to raise money from investors. That’s why it is important that you also should be thinking about how to put together a summary or short-form business plan that ranges anywhere from two pages to fifteen.
The shorter you can make your summary business plan the better it is by focusing on just a few key elements of your business that you feel will generate the most excitement among those reading it. You can always pass along a more detailed plan to those interested later.You don’t need to describe every feature or have detailed product designs.

How to Write a Summary Business Plan
A Few Don’ts: With that in mind, here are some suggestions for things to leave OUT of your summary business plan:
- Excessive market research: You need to do a tight analysis of your product or service and the competitors which you should be able to summarize it into one-page max.
- An overwritten product description: Don’t spend more than a paragraph on this.
- Detailed finances: it should be mentioned in the Bottom line
- How much money do you have?
- How much does it take to run the business?
- How much will you earn (hopefully)?
How to Write a Summary Business Plan: The Essential things that should be included to achieve what you DO want to focus on, consider the following tips:
Description: Kick off your plan with a one-page description of your business. Give a brief history of the business and its ownership structure by focusing on:
- Who you are
- What you do
- Where you are
Vision Statement: try writing a concise one or a two-paragraph vision statement, which gives the answer to the question: What do we want this company to become over the next five to 10 years?
Mission Statement: clearly mention the groundwork for your ‘brand promise’ in a one or two paragraph description of what your company will be to its customers.
Values: Provide a list of three to five core principles upon which you will build the business and stick to no matter what.
Goals: Make a list of three to five long-term goals that translate your company’s vision into specific, measurable, attainable, relevant and time-specific objectives.
Market research: Take the next two to three pages to briefly answer the following questions:
- What do you know about your industry?
- What do you know about your competition?
- Who is your target customer and what do you know about them (i.e. demographics, buying patterns)?
Market differentiation: Take the next page to detail what makes your product or service unique in the market by answering questions like:
- What makes you different from your competition that actually matters to your target customer?
- What is your unique value proposition?
- What is your big bold brand promise?
- Marketing message: Based on the answers you outline above, take the next half page to explain the message you plan to communicate to your target market.
- Marketing mix: Use the next page or so to detail the methods you will use to deliver that message.
- Measurement: Follow the previous two sections with another half-page describing how you will measure the effectiveness of each of those delivery methods and, based on the results, adjust your plan accordingly.
Sales: in the next full page summarize your sales plan by answering the following questions:
- What is your overall sales process?
- What are the specific steps in your process?
- How are leads generated?
- How are they researched/qualified?
- How do you get in front of your customer?
- How do you close the sale?
How will you achieve the optimal sales cycle?
Operations plan: Now, take one to two pages to answer the following questions:
- Who are the key players?
- What business process will you employ?
- What facility, equipment, and other resource needs are involved?
- How will you assure and measure quality and customer satisfaction?
- What are their backgrounds and qualifications?
- What are their specific roles?
- How will the business be organized (org. chart)?
- How will you produce the product or deliver the services?
- What are the logistics?
Personnel Plan: finish on one page the description of your plan by answering the questions like:
- What are personnel needed now to accomplish current goals?
- How will the number of people need to change with the growth of the business?
Financial Plan:
Your financial plans should be briefly explained in the same narrative style you have been using throughout the plan also, use a footnote to alert readers that more detailed financial schedules and assumptions will exist in a separate document. To keep focused, consider telling your story by providing the following information:
- Start-up costs, if applicable
- Revenue projections with detailed assumptions
- Three- to five-year cash-flow projections
- Three- to five-year balance sheet projections
Sources and uses of funds if you are raising capital.
What Should You Write In The Business Summary
A business summary, or management summary, is a short document or section of a document, produced for business purposes, that summarizes a longer report or proposal or a group of related reports in such a way that readers can rapidly become acquainted with a large body of material without having to read it all. It usually contains a brief statement of the problem or proposal covered in the major document(s), background information, concise analysis and main conclusions. It is intended as an aid to decision-making by managers and has been described as the most important part of a business plan.
A business summary differs from an abstract in that an abstract will usually be shorter and is typically intended as an overview or orientation rather than being a condensed version of the full document. Abstracts are extensively used in academic research where the concept of the business summary is not in common usage. “An abstract is a brief summarizing statement… read by parties who are trying to decide whether or not to read the main document”, while “a business summary, unlike an abstract, is a document in miniature that may be read in place of the longer document”.
A business summary template is a written statement which provides a review of a long report. It is written for non-technical people who cannot interpret the details of the in-depth report. It is also created for those professionals who don’t have time to read the complete report. It contains enough information for the reader to make him understand exactly what is described in the long report. All basic information is included in the business summary template in the same order with which they are placed in the long report. We have to try to cover all major ideas of the whole document in the business summary briefly. The business summary template generally used by business as a compact review of their working landmarks. Therefore, this smart summary will often outline the initial face of business for the facilitation of potential investors.
A well-written business summary is something that makes your report or business documents easy to understand so feel free to download and use following business summary template to write meaningful business summaries. A business summary is an important part of business writing that enables you to turn a big or lengthy business report or document into few lines so the reader can get an overall idea about the document or report at a glance. The business summary can also be explained as a document containing fewer lines or a particular section of a document or report and used, to sum up, a lengthier in such a way that readers can rapidly become familiar with the document without going through the whole reading.
A business summary is a brief introduction to a business plan. It should describe your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.
- Who you are.Start with your business’s name, location, and contact information.
- What you offer and the problem your business solves.Include a brief description of the product or service you offer and why it’s necessary. Your business doesn’t need to serve a larger social problem, but it should address a need or opportunity in the market.
- Your target market. Sometimes the product itself defines the market, such as “Peoria’s best Thai food,” or “Mini Cooper dashboard accessory.” If not, then a brief description of the target market.
- Business plan purpose. Say whether you’re seeking investment or trying to secure a bank loan. A business summary is only really necessary when you are sharing your business plan with outsiders.
- Size or scale. For example, with an existing company, that information might be as simple as adding recent annual sales or number of employees to the basic company information in the first bullet here. For a startup, it might be a brief description of aspirations, such as a sales goal for the next year or three years from now. I often recommend a simple highlights chart, a bar chart with sales and gross margin for the next three years.
- Critical details. Mention any defining details that would matter to the person that will ultimately read the summary–like that the founders are all MBA students at the local university, or that your business has been awarded a prestigious development grant. Remember, some readers will only look at the summary of your business plan.
The information you need to include varies somewhat depending on whether your business is a startup or an established business.
For a startup business typically one of the main goals of the business plan is to convince banks, angel investors, or venture capitalists to invest in your business by providing startup capital in the form of debt or equity financing. In order to do so, you will have to provide a solid case for your business idea which makes your business summary all the more important.
A typical business summary for a startup company includes the following sections:
- The business opportunity – describe the need or the opportunity.
- Taking advantage of the opportunity – explain how your business will serve the market.
- The target market – describe the customer base you will be targeting.
- Business model – describe your products or services and what will make them appealing to the target market.
- Marketing and sales strategy – briefly outline your plans for marketing your products/services.
- The competition – describe your competition and your strategy for getting market share. What is your competitive advantage, e.g. what will you offer to customers that your competitors cannot?
- Financial analysis – summarize the financial plan including projections for at least the next three years.
- Owners/Staff – describe the owners and the key staff members and the expertise they bring to the venture.
- Implementation plan – outline the schedule for taking your business from the planning stage to opening your doors.
For established businesses the business summary typically includes information about achievements, growth plans, etc. A typical business summary outline for an established business includes:
- Mission Statement– Articulates the purpose of your business. In a few sentences describe what your company does and your core values and business philosophy.
- Company Information – Give a brief history of your company – describe your products and/or services, when and where it was formed, who the owners and key employees are, statistics such as the number of employees, business locations, etc.
- Business Highlights– describe the evolution of the business – how it has grown, including year-over-year revenue increases, profitability, increases in market share, number of customers, etc.
- Financial Summary – if the purpose of updating the business plan is to seek additional financing for expansion, then give a brief financial summary.
- Future goals – describe your goals for the business. If you are seeking to finance explain how additional funding will be used to expand the business or otherwise increase profits.
20+ Business Summary Templates, Samples, Examples
Business summary templates are quite popular among the companies that are looking for fresh investments in the business proposals. Compiling numerous sets of data into two or three pages is not an easy task as it requires the services of the specialists. With the use of the business summary templates, the companies can make the whole process a breeze and impeccably efficient. It will not only provide a clear picture to the investor but also reduce the expenditure.
Business summaries are generally prepared for higher authorities and business employees of the company because they have not enough time to read complete business reports or documents. Business summary if written well, tells the reader that what is included in the report or document and what is the basic purpose of writing. Business summaries also provide a writer great way to make a lengthy business presentation or plan easily understandable for preparations prior to business meetings and seminars.
The business summary is written to indicate main points and parts of the large report or document. For example, when you are making a business plan for your existing business or company, a business summary of the business plan briefly tells investors and shareholders that where your company is, where you want to take it in near future and why the expresses business plan or idea is worthy of the business development. Contents of business summaries can vary from each other as these are prepared for different purposes. Here we have added a free business summary template which is loaded with all basic points and info that must be there in a summary report.
It is a crucial document is actually served as a first & right impression of your business. However, the business summary format will help the business to convey their business plan, strategies & policies in an intuitive manner. There is no need of writing a huge article which will be impossible for others to fully readable. The business summary template will assist the business to grab the interest of investor within few seconds. Undoubtedly, a business summary will explain the essence & total energy of business plan in a clear and compelling way. This format is our best example of professional work and high quality. It does not matter whether you are using it for personal purpose or business purpose, it is perfect for every kind of use. The printable setting of this business summary is by default settings and there is no need to waste time on this. We are providing one format at one time; therefore we shall discourage our users to use it same as it given.
For business people, the business summary will serve as a condensed paragraph of a report or a problem in which the reader will surely comprehend the whole and long content of the topic while reading it. The shortening tool you can print by any writer can write the main thought of their Summary Report so the reader or audience will easily acquaint to what is the issue is all about.
- Sample Business Summary Template: The sample business summary template consists of numerous sections such as business and the financial data that can have an overall impact on the decision making of investors. It is a well-known fact that provides a snapshot of the performance of the company by providing crucial guidelines to the business and the managers.

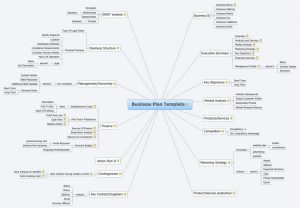
- Business Plan Template: It consists of three sections namely business summary along with company, products, and services. In addition, a header section comprising of marketing opportunity is also added to the eclectic mix. The summary statements are already prepared for the users. They only required entering relevant information in the template without any problem and confusion.

- Printable Business Plan Summary Template

- Business Summary Template: The template comprises of business summary which provides detailed information about the project, the associated threats, and opportunities in the future. It is bound to provide amazing results in the long run. There are different sets of objective headings that could be used to indicate the purpose in an easy and hassle-free manner.

- Download Business Summary Template: The business summary template consists of company background header, product and service description along with other sections that would be difficult to design from the ground up.

- Free Business Plan Template
- Simple Business Summary Template

- Word Download Business Summary Template
Business Summary Template Free DownloadCompanies seeking capital often ask how long the Business Summary of their business plan should be. The answer depends upon the use of the summary, mainly determining if
- it precedes the full business plan, or
- it will be used as a stand-alone document.

When the Business Summary precedes the business plan, its length should be short, typically only one to two pages and certainly no longer than three pages. This is because the Business Summary is not meant to tell the whole story of the business opportunity. Rather, the summary must simply stimulate and motivate the investor to learn more about the company in the body of the plan.
The second type of Business Summary is a stand-alone document. That is, it is given, by itself, to investors for their initial review. If interested, the investor will then request the full business plan. A stand-alone Business Summary is often used to limit the flow of information. That is if an investor is not interested in the general opportunity that your summary presents, you don’t want to reveal to them intimate details of your plan.
Companies seeking capital often ask how long the Business Summary of their business plan should be. The answer depends upon the use of the summary, mainly determining if
- it precedes the full business plan, or
- it will be used as a stand-alone document.
When the Business Summary precedes the business plan, its length should be short, typically only one to two pages and certainly no longer than three pages. This is because the Business Summary is not meant to tell the whole story of the business opportunity. Rather, the summary must simply stimulate and motivate the investor to learn more about the company in the body of the plan.
The second type of Business Summary is a stand-alone document. That is, it is given, by itself, to investors for their initial review. If interested, the investor will then request the full business plan. A stand-alone Business Summary is often used to limit the flow of information. That is if an investor is not interested in the general opportunity that your summary presents, you don’t want to reveal to them intimate details of your plan.
Regardless of which type of Business Summary you are developing, the summary must include the following critical elements:
- A concise explanation of the business
- A description of the market size and market need for the business
- A discussion of how the company is uniquely qualified to fulfill this need: In addition, a stand-alone Business Summary should include summaries of each essential element of the business plan. This includes paragraphs addressing each of the following:
- Customer Analysis: What specific customer segments the company is targeting and their demographic profiles.
- Competition: Who the company’s direct competitors are and the company’s key competitive advantages.
- Marketing Plan: How the company will effectively penetrate its target market.
- Financial Plan: A summary of the financial projections of the company.
- Management Team: Biographies of the key management team and Board members.
- The Business Summary is the most critical element of the business plan. If it does not grab the investor’s attention, the investor will neither read nor request the full business plan. As such, spend time developing the best possible summary, create two versions (e.g., stand-alone and full plan predecessor) as appropriate, and work to get it in the hands of the right investors.







